A
black hole is a result of a very
massive star that
has collapsed on itself. The gravity influence of
such an object is so great that light cannot escape.
We can measure the effects of a
black hole and we
can also determine the dimensions of a
black hole.
There is only a center and a surface to a
black hole:
- The center of a
black hole is called a
"singularity"
- The surface of a
black hole is called the
"event horizon"
The event horizon is almost like a point of no
return. To determine the distance from the
singularity to the even horizon, the Schwarzschild
Radius equation is used:
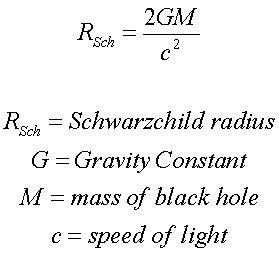
Back to Top
|

